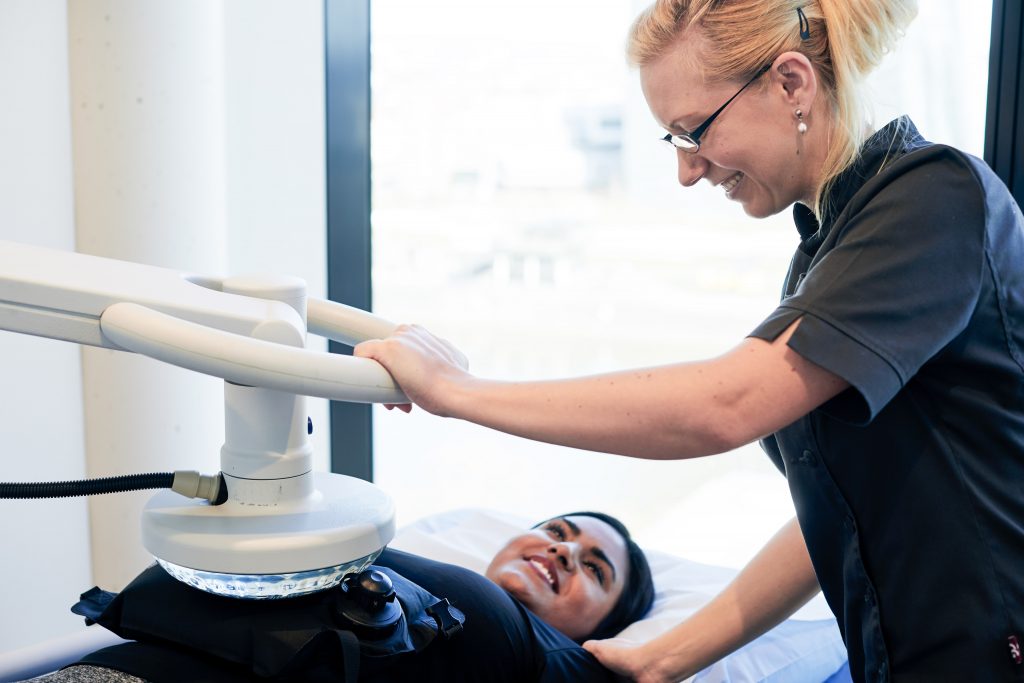
Regional Hyperthermia
Regional Hyperthermia
HOW REGIONAL HYPERTHERMIA MAY HELP YOU
What is Regional Hyperthermia?
Regional hyperthermia is a treatment for combating cancer. As tumorous matter is less effective than healthy tissue at diverting heat, they can be easily affected by marginal changes in temperature. The high-power hyperthermia applicator heats up tissue to a temperature of approximately 105 degrees with short radio waves.
Healthy tissue is largely unaffected, but cancerous tissue overheats and its ability to absorb oxygen plummets. As a result of the heat, it forms heat shock proteins on its surface, which the body’s immune system can recognize as foreign agents and destroy. Hyperthermia therapy can be combined with many other modalities as part of a more effective treatment program.
Since the days of Hippocrates, physicians have been using heat as a form of cancer therapy. How does this work? Simply put: Cancer doesn’t like heat. In fact, once cancer cells are heated above approximately 105oF their metabolism starts to break down. This halts further growth and causes the cells to die. For the cancer sufferer, that means tumor shrinkage and slower progression of the disease.
While superficial tumors can readily be exposed to higher temperatures, the real science is in reaching these temperatures inside the body, without damaging the surrounding healthy tissue. The solution to this problem began with the research and discovery of electromagnetic energy at the beginning of the 19th century.
It was shown that high amounts of energy could be applied to the human body using electromagnetic fields. In the last 30 years, the use of regional hyperthermia in cancer treatment has reached its most advanced state. Modern regional hyperthermia uses radio waves to reach high temperatures within the tumor tissue.
Hyperthermia generally enhances the effects of other forms of tumor therapy. Hyperthermia can thus substantially improve the effects of conventional therapies.
As a result of numerous research efforts and clinical studies, it has been shown that overheating a tumor can lead to growth inhibition, tumor shrinkage, and even healing.
Due to the nature of tumor cells, these tend to heat up much faster than healthy cells. They also react very differently to heat exposure. A rise in temperature causes a change in the proteins of tumor cells. This can be likened to heating an egg. The protein in the egg white changes its form and goes from clear and runny to white and firm.
Of course, this is a little too simple to describe the process in a cancer cell, but it helps paint a picture of what a “heat shock protein” is. These heat shock proteins appear on the surface of cancer cells but not on healthy cells. Regional hyperthermia thus helps differentiate healthy cells from cancerous ones, making the cancer cells easy targets for the immune system.
While the heat is getting to work on the tumor, the surrounding healthy cells are enjoying increased blood flow with all its benefits. As a patient, you may feel some gentle local heat, but really not much more.
Possible Regional Hyperthermia Benefits
- Increased permeability for anti-cancer agents
- Better visibility for the immune system due to heat shock proteins
- Gentle and selective treatment
- Increase the effects of radiation or chemotherapy
- Tumor shrinkage due to cancer cell apoptosis
- Localized inflammatory and immune activity
Who Can Benefit from Regional Hyperthermia?
Anyone with any type of tumor can benefit from regional hyperthermia. These include sarcoma, melanoma, and mesothelioma, as well as cancers of the head and neck, brain, lung, esophagus, breast, bladder, rectum, liver, appendix, and cervix.
Regional hyperthermia is often combined with other cancer treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy. Regional hyperthermia can be used to make some cancer cells more sensitive to radiation, or to harm cancer cells that radiation cannot damage. It can also be used to enhance the effects of certain anticancer drugs.
There are numerous studies and clinical trials on the use of regional hyperthermia; many have shown a significant reduction in tumor size when hyperthermia is combined with other treatments.
Regional hyperthermia is commonly used as part of an integrative or biological treatment approach in patients who do not wish to undergo radiation or chemotherapy.
Unlike surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, hyperthermia has almost no side effects. After treatment, some tiredness can occur. In rare cases, the increased death of malignant cells can result in slight fever spikes.
In some cases, patients who have tumors in the vicinity of hip or knee replacements may require an adjusted protocol as the metals can heat up excessively under the influence of electro-hyperthermia.
Sweat accumulation under the electrodes can cause excessive reactions resulting in skin burns. This can be avoided by placing a thin layer of absorbent material between the skin and the electrode.
Cardiac pacemakers and other pacemaker electrodes may result in functional disruptions and destruction of the pacemaker’s electronics.
Regional hyperthermia has almost no side effects, and can be used as part of a treatment regimen for most tumor forming cancers, such as:
- Bladder cancer
- Breast cancer
- Brain Cancer
- Cancer of the appendix
- Cancer of the cervix
- Cancer of the peritoneal lining
- Cancers of the head
- Cancers of the neck
- Colorectal cancers
- Esophageal cancer
- Liver cancer
- Lung cancer
- Melanoma
- Prostate cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Sarcoma
Contraindications
Patients with one or more of the following conditions are not suitable candidates to receive regional hyperthermia treatment:
- Open Wounds
- Scar Tissue
- Epilepsy
- Anesthesia
- Pacemaker
- Metal implants
- Bone Marrow Transplants
- Pregnancy
How is Regional Hyperthermia Performed?
Regional hyperthermia is usually applied for 60 minutes to a single area. A complete treatment protocol typically consists of 12 applications. As with all therapies, the exact dosage and number of applications is adjusted to meet the needs of each individual.
Regional Hyperthermia Frequently Asked Questions
What Types of Hyperthermia are There?
First of all, it is useful to make the distinction between active and passive hyperthermia. The aim of active hyperthermia, which is also called fever therapy, is to increase the body temperature using bacterial toxins or by influencing the cytokines.
However, today the term “hyperthermia” is usually used in connection with passive hyperthermia which introduced or induced heat externally. Different applications of hyperthermia include:
Whole-body hyperthermia
Usually performed under general anesthesia the full body is exposed to heat. Used for immune stimulation and treatment of tumors/metastases that have spread to multiple organs or systemic tumor illnesses.
Surface hyperthermia
Treating skin tumors and metastases (included in Celsius TCS system)
Regional deep hyperthermia
To treat solid tumors in organs such as the liver, lungs, brain, pelvic area and the like (Included in Celsius TCS system)
Perfusion hyperthermia
For hyperthermal perfusion of metastasized hollow organs or spaces
Which Types of Tumors Can Regional Hyperthermia Be Used?
Regional Hyperthermia is indicated for the treatment of solid tumors in curative and palliative therapies, including:
- Gynaecological malignancies (e.g. breast, ovary, cervix etc.)
- Malignant tumors in organs
- Deep seated cancer lesions (e.g. brain, liver, lung, kidney, pancreas, etc.)
- Lymph node metastases
- Gastrointestinal tumors (e. g. esophagus, colon etc.)
- Sarcomas, melanomas, basaliomas, etc.
What are the Side Effects of Regional Hyperthermia? Is the Treatment Painful?
In contrast to surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, hyperthermia has almost no side effects. On the contrary: patients often report feeling the positive, calming benefits of the heat. They regularly report a “calming” sensation and reduced stress.
Some tiredness can occur after treatment. In rare cases, the increased death of malignant cells can result in slight fever spikes. In general, however, this is considered to be a positive physical sign.
Patients with a disrupted perception of temperature (for example following a stroke) must be observed constantly during treatment. The hyperthermia area must be monitored continuously throughout the procedure (i.e. to avoid sweat accumulation; sweat can heat up excessively and result in blisters on the skin). Otherwise, every patient is given a push-button that can be used at any time to interrupt the treatment if he/she feels an uncomfortable heat sensation.
Why is Regional Deep Hyperthermia Suitable as a Complementary Method to Radiation Therapy?
Different mechanisms are responsible for the supra-additive effect of hyperthermia when used in conjunction with radiotherapy. The additive, complementary effect of hyperthermia is due to the higher heat sensitivity of cells in the S phase, which are relatively radio-resistant.
Hyperthermia can also cause increased blood flow and thus increased tissue oxygenation, which results in increased radio-sensitivity. Therefore, it is best to perform hyperthermia before or during radiotherapy; alternatively, hyperthermia can also be administered immediately after radiation.
Hyperthermia increases cytotoxic radiation effects, particularly by interfering with the cellular repair system as a result of the denaturing of the DNA. In vivo studies have shown that hyperthermia can boost the effect of radiotherapy by a factor of 1.2 to 5. Hyperthermia is probably the most potent radio-sensitizing method currently known.
Regional Hyperthermia as a Complementary Treatment to Radiotherapy
The primary mechanism of radiotherapy is the generation of free oxygen radicals by ionizing radiation, which in turn attack the DNA of tumor cells. Cells low in oxygen are three times more resistant to gamma radiation than normal cells. This is where hyperthermia can be a complementary treatment.
Due to the heating of the tissue, blood flow increases, resulting in higher oxygen enrichment in the affected tissue. Another important effect is the inhibition of the cancer cells’ own DNA repair mechanisms because the heat releases heat-shock proteins. Thus, hyperthermia is probably the most effective support to radiotherapy available today.
Is Regional Deep Hyperthermia Suitable as a Complementary Treatment to Chemotherapy?
Hyperthermia is normally administered in parallel with chemotherapy. Hyperthermia generally enhances the effects of chemotherapy on the tumor. The most important reason for this is that capillary vessels in the tumor tissue generally have no muscle layer (steel phenomenon) and thus are not able to expand when overheated, unlike the micro vessels in adjacent healthy tissue.
Since under normal temperature conditions during chemotherapy a higher blood flow occurs in the tumor tissue first, the cytostatic drugs in the tumor tissue diffuse more strongly. With the subsequent targeted hyperthermia of the tumor region and the adjacent healthy tissue, the blood flow ratio changes such that the drugs in the tumour tissue cannot be flushed out as easily, and at the same time blood perfusion in the surrounding healthy tissue is now higher and thus the cytostatic drugs can be evacuated more easily.
Furthermore, the permeability of the capillary vessels in the tumor is increased by the insufficient (lack of) wall build-up under the influence of heat, thus accelerating the absorption of cytostatic drugs by the cancer cells.
Thus, in some cases, previously ineffective chemotherapy can become an effective treatment thanks to hyperthermia.
Regional Hyperthermia as a Complementary Treatment to Chemotherapy
Confirmed by the results of a new study, it has been shown that hyperthermia has a significantly stronger impact compared to pure chemotherapy (e.g. Issels 2007 for sarcomas; Jones 2007 for breast cancer, among others).
The technique of regional deep hyperthermia heats up the tumor cells using high-frequency waves and affects the metabolism of the cells and the extracellular environment.
This causes the cellular metabolism of the cancer cells to change locally to such an extent that programmed destruction can be induced (apoptosis).
Meanwhile, it has been proven repeatedly that heating a tumor can inhibit the growth of tumor cells, shrink tumors and even result in complete healing.
Does Statutory Insurance Pay for Celsius TCS – Tumor Cell Solution Treatment?
Since regional electro deep hyperthermia is an innovative and new form of therapy, in accordance with §12 of the German SGBV, health insurance companies are not obligated to pay for it. However, an application for reimbursement can be lodged. Following a decision by the German Federal Court of Justice (BGH) in August 2006 *, an insurance agency was ordered to cover the treatment costs in an individual case. Otherwise, the costs for regional deep hyperthermia are normally billed at the simple rate of the German scale of charges for doctors (GOÄ) (according to GOÄ Section 5854 (145.14 Euro) per treatment session).
What is the Essential Advantage of Infusio’s Hyperthermia System?
The Celsius TCS system is equipped with two active electrodes, which sets it apart from other systems
currently on the market. Our technical innovation ensures that the tumor is subject to a more homogeneous temperature development. Thanks to the various electrode sizes, the target area in the patient’s body can be heated up precisely.
The various levels of impedance (“sensitivity”) in the diseased and healthy tissue therefore further support the treatment focus.
Tumors located deeper within the body can be treated as well. This is accomplished by a carrier frequency of 13.56 MHz, which is generally able to reach even deeper-lying regions. At the same time, the powerful high capacity generated by the intelligent technical impact and a particularly sustainable water-cooling system ensure a significant penetration depth.
Does the Celsius TCS – Tumor Cell Solution have a valid CE Certification according to the Medical Products Law?
Yes, Celsius TCS – Tumor Cell Solution is certified in the more stringent MPG Class IIb and has corresponding CE certification.
*FAQ Source: https://www.celsius42.de/en/faq
Resources
General Resources
Scientific Articles
Regional Hyperthermia for cancer
Combinations in multimodality treatments and clinical outcomes during cancer (Review)
Adjuvant therapy in pancreatic cancer
Hyperthermia: How Can It Be Used?
Review: The Role of Hyperthermia in Treating Pancreatic Tumors
A Systematic Review of Regional Hyperthermia Therapy in Bladder Cancer
Current state of the art of regional hyperthermia treatment planning: a review